What is the difference between analysis and analytics? While many people use these terms interchangeably, they actually have distinct meanings and applications. Both involve data, but their roles in decision-making and problem-solving differ. In this blog post, we will explore their key differences, significance, and the various forms of analytics used across different domains.
What is Analysis?
Analysis is the action of breaking down complex data or problems into parts small and simple enough to understand some patterns, trends, or relationships. It is often a backward-looking process focused on the analysis of past data to extract insights of significance.
Characteristics of Analysis
- Involves examination of historical data
- Assists with the identification of patterns and trends
- Provides insight for decision making
- Usually employed for problem-solving and root-cause identification
Example : The sales manager analysing past quarter revenues to find reasons for the decline in sales is an example of analysis.
What are Analytics?
Analytics constitutes the systematic study of statistical, mathematical, and computational techniques to analyse data to forecast behaviour and optimize decisions. Its growth trajectory was laid down by the real-time processing of data and predictive modelling as precursors to strategic action.
- Combines modelling of data, machine learning, and algorithms
- Forecasting/predictive insight is the priority
- Assists in process optimization and decision-making
- Establishes automation and AI-enabled tools.
Example: A retail company analyses the purchase history of customers and recommends products using AI-based analytical systems.

Key Differences Between Analysis and Analytics
| Aspect | Analysis | Analytics |
| Focus | Past data | Predictive and real-time insights |
| Purpose | Understanding trends and patterns | Forecasting and decision optimization |
| Techniques | Statistical methods, descriptive analysis | Machine learning, predictive modelling |
| Example | Examining customer feedback to find common complaints | Using AI to predict customer preferences |
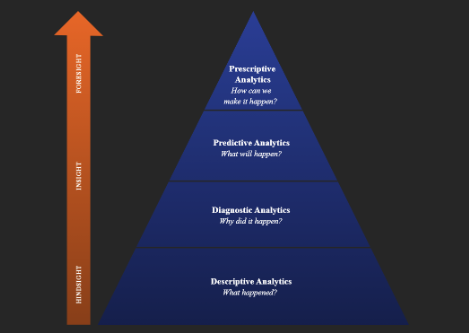
Types of Analytics
Analytics might be generally classified into four types
1. Descriptive Analytics
This type summarizes historical data with the intent of identifying trends and pattern results. For example, monthly sales reports showing revenue trends.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
This type allows one to figure out why something happened in the past. For example, analysing customer churn to understand reasons for drop-offs.
3. Predictive Analytics
Uses machine learning and statistical modelling to foresee future outcomes. For example, stock market trends predicted based on historical data.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
Gives recommendations about what to do best based on data insights. AI recommendation engines suggest products to customers, for example:
Conclusion
Though analysis and analytics pertain to data, they are different concepts altogether. Analysis entails examining past trends, while analytics uses data to make forecasts and inform present-day decision-making better. Understanding the difference between analysis and analytics is crucial, especially as industries become more data-centric. This shift has also increased the demand for data science professionals which includes various Data Science roles and skills.
